The Science Behind UV-C Energy: What Is It? - UV Resources
UV light comprises a segment of the electromagnetic spectrum between 400 and 100 nm, corresponding to photon energies from 3 to 124 eV. The UV segment has four sections, labeled UV-A (400 to 315 nm), UV-B (315 to 280 nm), very high energy and destructive UV-C (280 to 200 nm), and vacuum UV. Most of us are familiar with the harmful effects of UV energy transmitted by sunlight in the UV-A and UV-B wavelengths, giving rise to UV “sunburn” inhibitors, or blocking agents, which are found in glasses and lotions. We are also familiar with products engineered to withstand the effects of UV radiation, such as plastics, paints, and rubbers. However, unlike the UV-A and UV-B wavelengths, the UV-C band has more than twice the electron volt energy (eV) as UV-A, and it is well absorbed (not reflected) by organic substances, adding to its destructiveness.
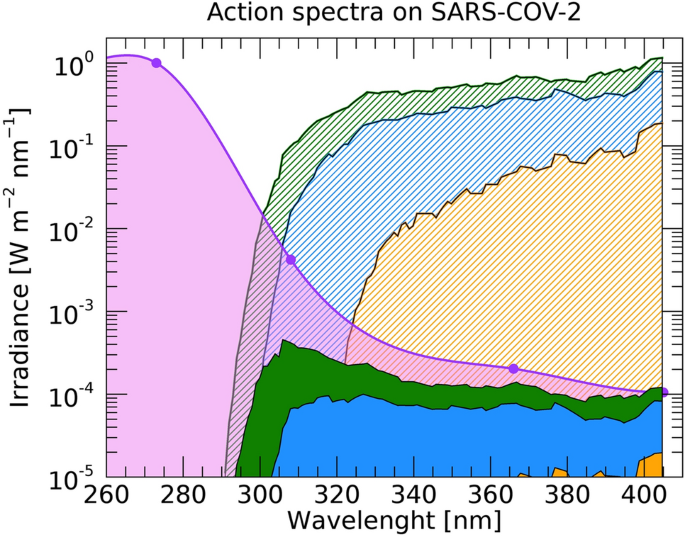
Solar UV-B/A radiation is highly effective in inactivating SARS-CoV-2

The Science Behind UV-C Energy: What Is It? - UV Resources
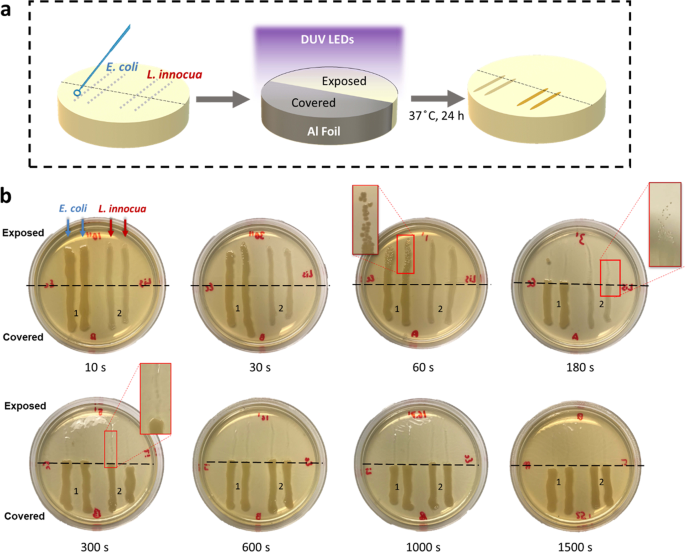
Inactivation of Listeria and E. coli by Deep-UV LED: effect of substrate conditions on inactivation kinetics
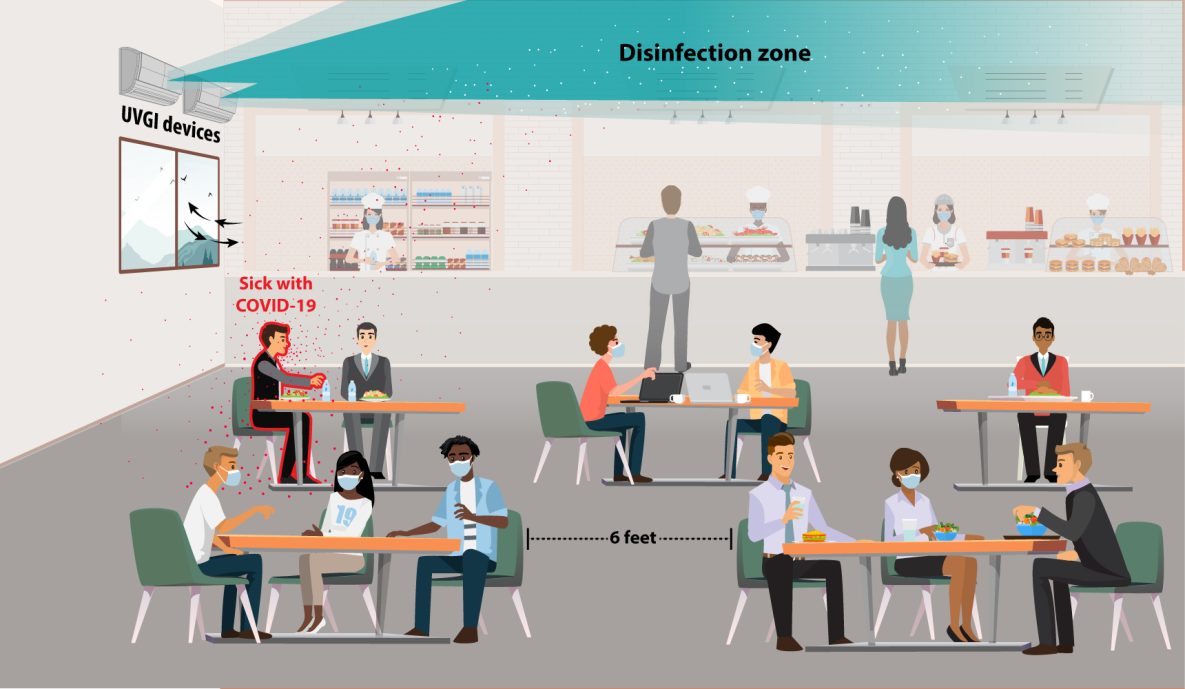
Upper-Room Ultraviolet Germicidal Irradiation (UVGI)
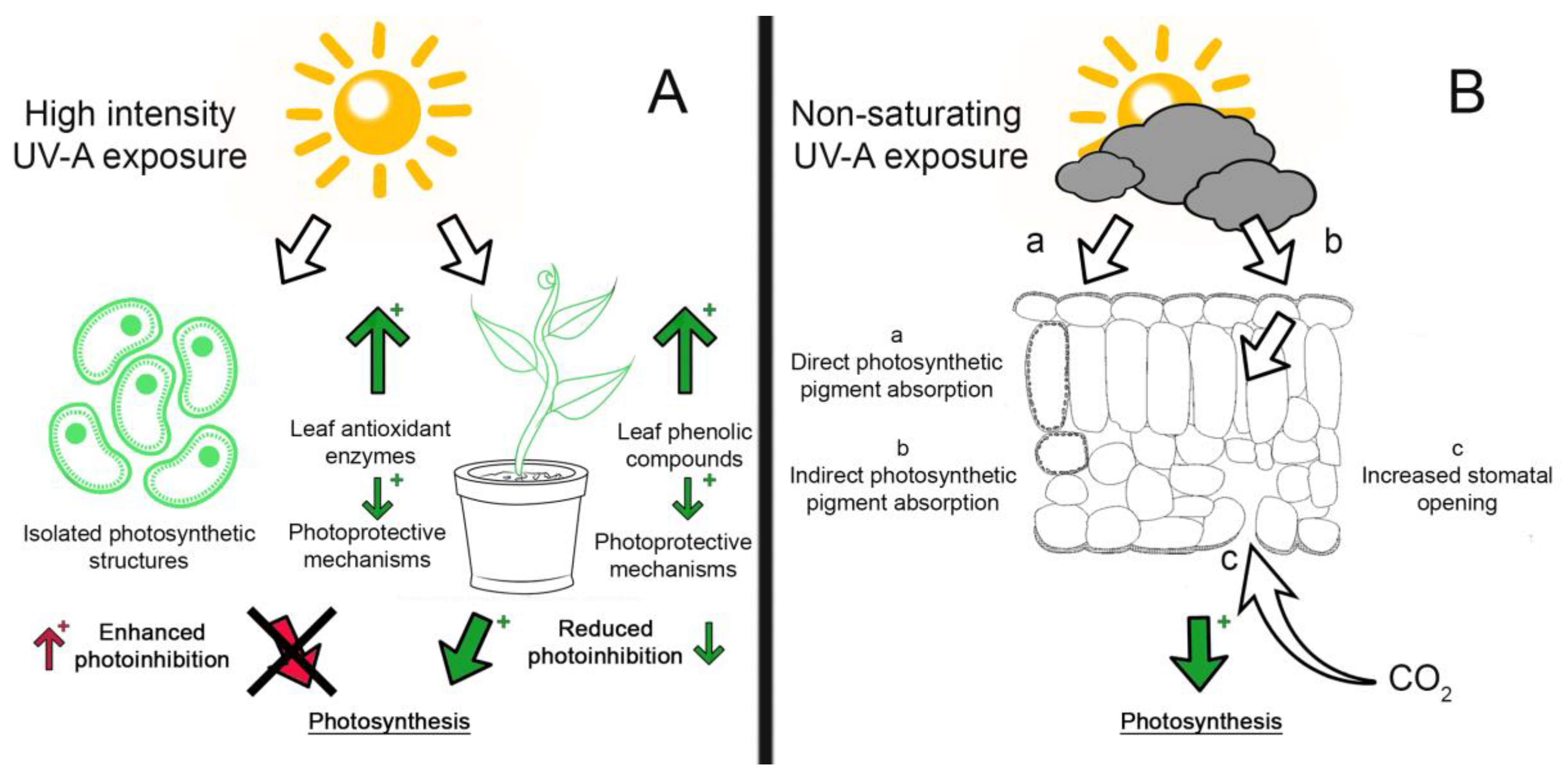
Horticulturae, Free Full-Text

Ultraviolet C irradiation: A promising approach for the disinfection of public spaces? - ScienceDirect

Ultraviolet Radiation, Definition, Uses & Examples - Video & Lesson Transcript
Ultraviolet Waves - NASA Science

Type of ultraviolet light most effective at killing coronavirus is also the safest to use around people