Current flow during tACS. When current is applied sinusoidally, the
Download scientific diagram | | Current flow during tACS. When current is applied sinusoidally, the direction of current flow flips back and forth by 180˚for180˚for every half-wave. Let us consider the left stimulation electrode. During the positive half-wave, it represents the anode of a tDCS stimulation with from publication: Finite-Element Model Predicts Current Density Distribution for Clinical Applications of tDCS and tACS | Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) has been applied in numerous scientific studies over the past decade. However, the possibility to apply tDCS in therapy of neuropsychiatric disorders is still debated. While transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) has been | Transcranial direct current stimulation, tDCS and Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.

Biohacking : tACS Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation Demystified

The impact of gamma transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS) on cognitive and memory processes in patients with mild cognitive impairment or Alzheimer's disease: A literature review - ScienceDirect
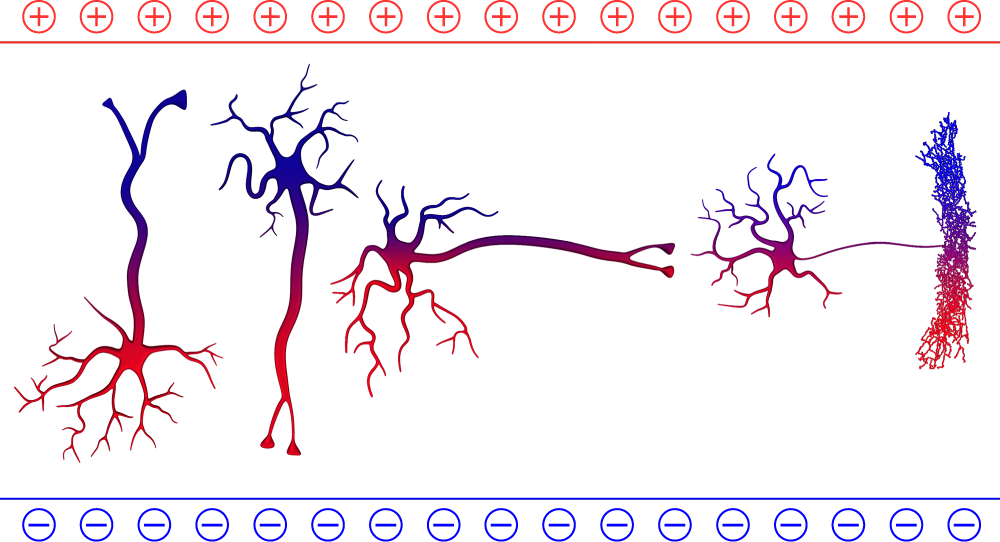
Immediate neurophysiological effects of transcranial electrical stimulation

Mapping entrained brain oscillations during transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS) - ScienceDirect
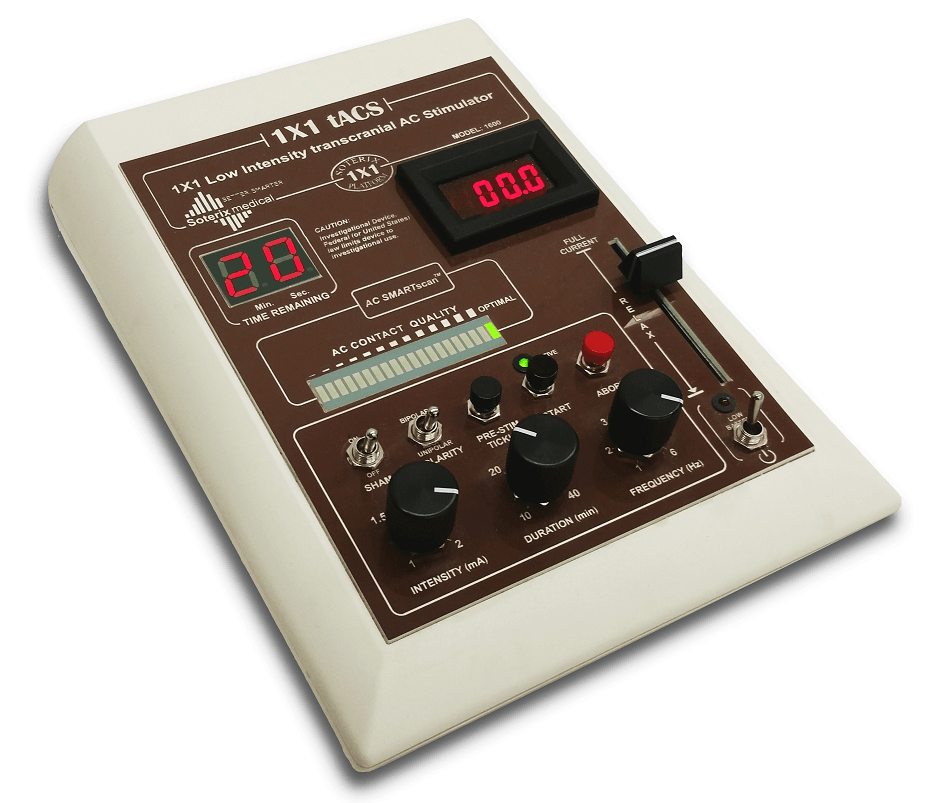
1x1 tACS Device - Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation – Soterix Medical

Transcranial Electrical Stimulation: Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS), Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation (tACS), Transcranial Pulsed Current Stimulation (tPCS), and Transcranial Random Noise Stimulation (tRNS) - ScienceDirect

Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation - an overview

PDF) Finite-Element Model Predicts Current Density Distribution for Clinical Applications of tDCS and tACS
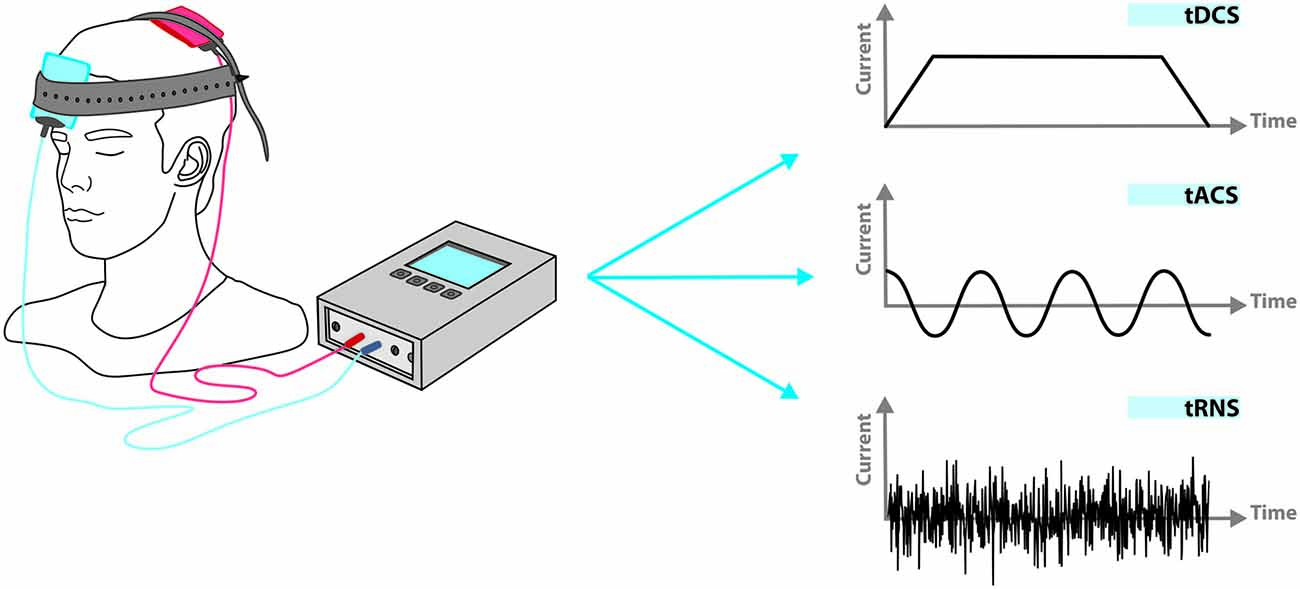
Frontiers Transcranial Electric Stimulation for Precision Medicine: A Spatiomechanistic Framework