dg.differential geometry - Determining a surface in $\mathbb{R}^3$ by its Gaussian curvature - MathOverflow
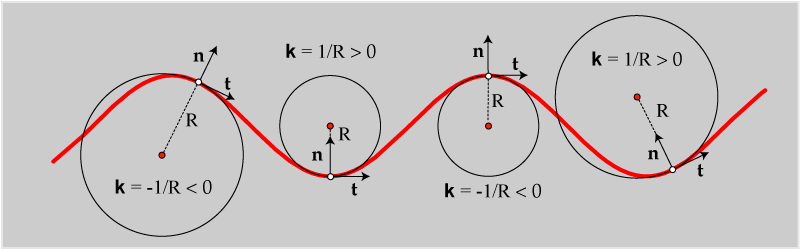
A curve in the plane is determined, up to orientation-preserving Euclidean motions, by its curvature function, $\kappa(s)$. Here is one of my favorite examples, from Alfred Gray's book, Modern

Differential Geometry: Lecture 12 part 1: surfaces in R3

PDF) Non-existence of orthogonal complex structures on the round 6

Distance distributions and inverse problems for metric measure

Differential Geometry: Lecture 21 part 2: total Gaussian curvature

Distance distributions and inverse problems for metric measure

Differential Geometry: Lecture 16: calculation of K and H
introduction.html
What are applications of convex sets and the notion of convexity

Lecture 15: Curvature of Surfaces (Discrete Differential Geometry

Lecture 15: Curvature of Surfaces (Discrete Differential Geometry

Curvature of a surface, only using calculus

Visual Differential Geometry & Forms

CS 15-458/858: Discrete Differential Geometry – CARNEGIE MELLON








