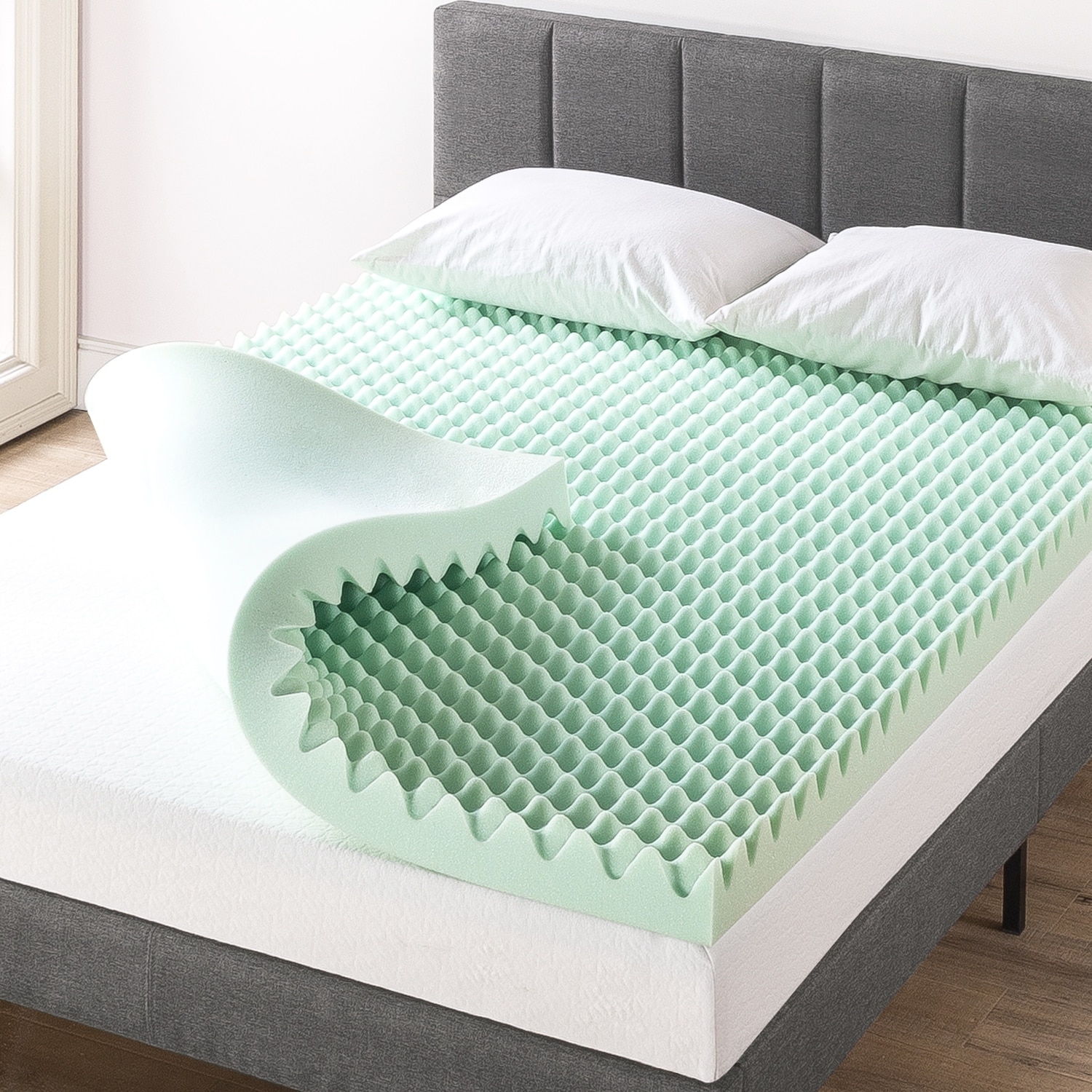
Wool: History, Processing, Types and Benefits: - Pressure Sore Prevention & Treatment
Are you aware that wool comes from a variety of animals? Do you want to know about the history of wool? If so, then here goes! Continue reading to learn about wool, its varieties, uses, and advantages.
If you are looking to buy Australian Medical Sheepskin products, you are in the right place. All of our medical sheepskins are natural and premium quality. Down-Under Wool specializes in the use of Australian Medical Sheepskin for Pressure Sore Prevention. We are specialists in the supply of medical bed underlays. overlays and medical sheepskins. We have a reputation for supplying only the very best Australian lambskin and medical sheepskin products. Our primary focus has always been on the repeatability of the product’s quality and craftsmanship

Using complementary and alternative medicines to prevent and treat pressure ulcers: a systematic review

Device-related pressure ulcers: SECURE prevention

Understanding Pressure Ulcer Research and Education Needs: A Comparison of the Association for the Advancement of Wound Care Pressure Ulcer Guideline Evidence Levels and Content Validity Scores
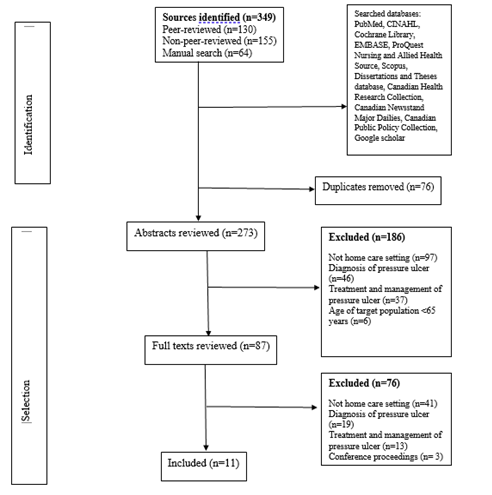
Home-Health-Aides Role in Preventing Pressure Ulcers of the Older Adults: a Scoping Literature Review
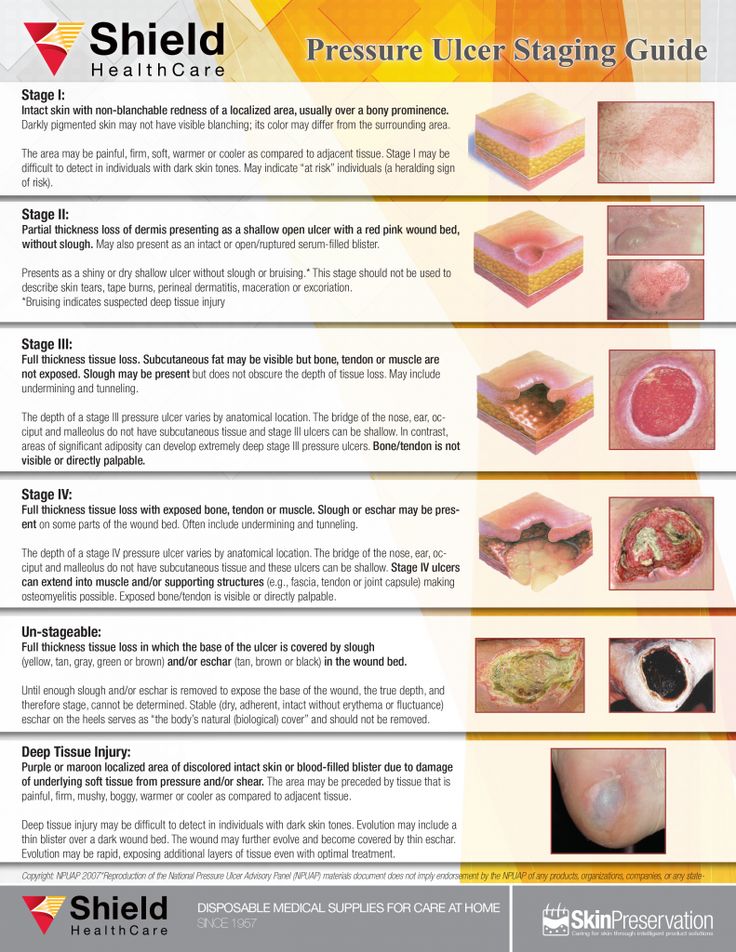
Bed sore antibiotic treatment
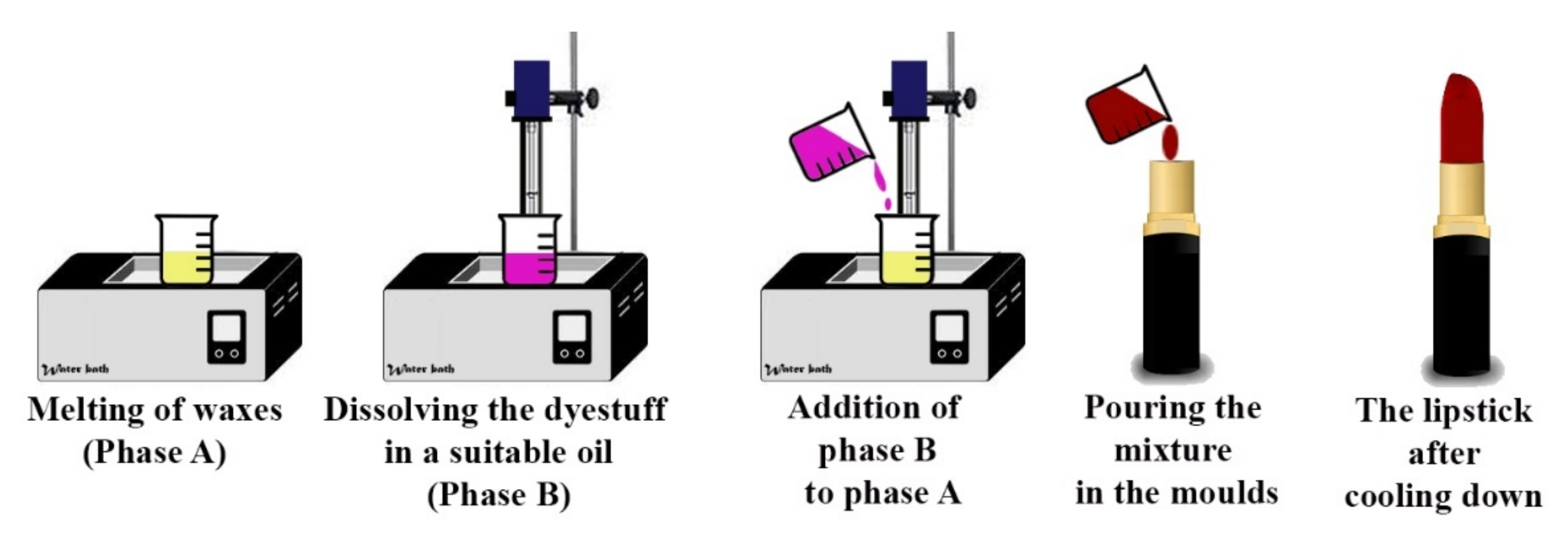
Cosmetics, Free Full-Text
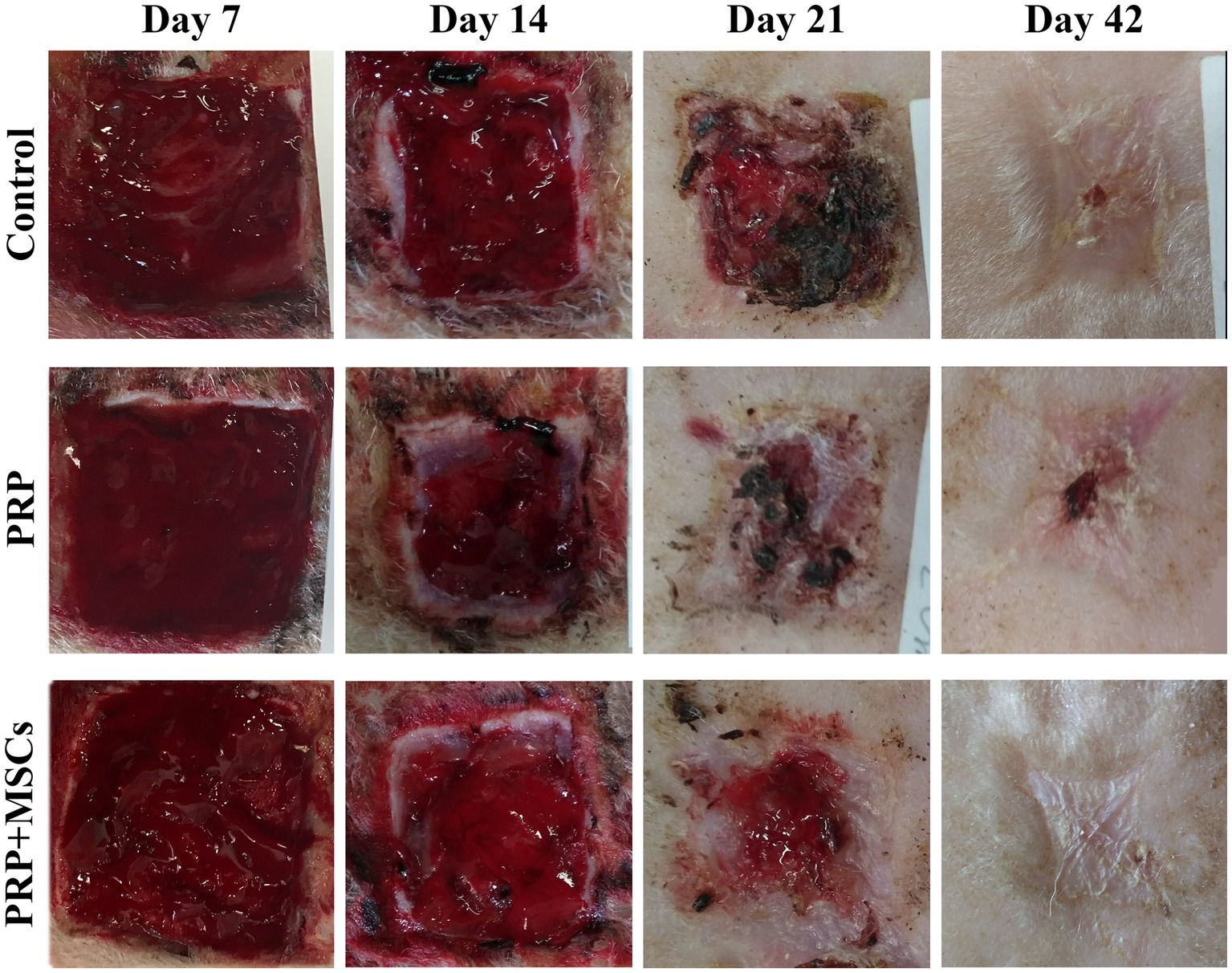
Frontiers Assessment of the quality of the healing process in experimentally induced skin lesions treated with autologous platelet concentrate associated or unassociated with allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells: preliminary results in a
Expert advise for Pressure Sore Prevention

Factors causing Decubitus Ulcers

Wool Compression Socks: The Pros & Cons

A Randomized, Controlled Study to Assess the Effect of Silk-like Textiles and High-absorbency Adult Incontinence Briefs on Pressure Ulcer Prevention

Bedsores (pressure ulcers) - Symptoms and causes - Mayo Clinic









