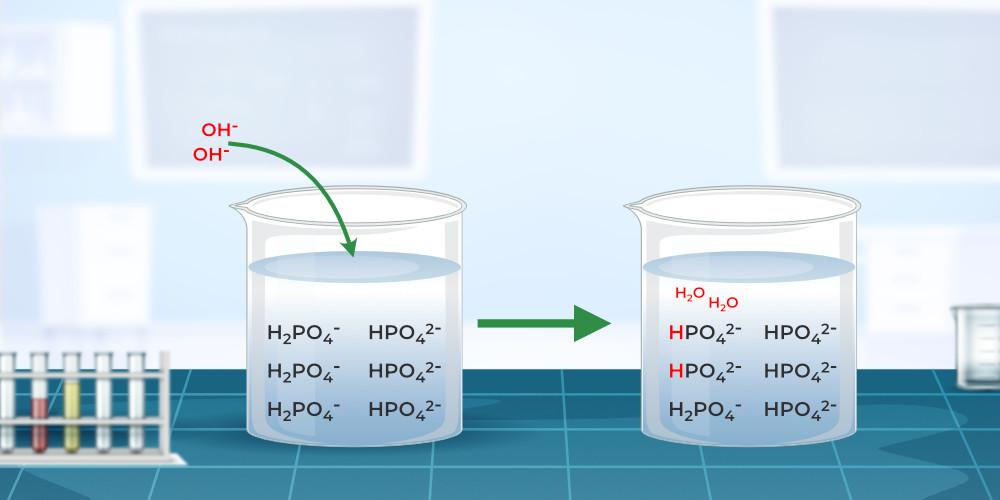
Buffer, pH control, acid-base balance, buffer solutions
Buffer, in chemistry, solution usually containing an acid and a base, or a salt, that tends to maintain a constant hydrogen ion concentration. Ions are atoms or molecules that have lost or gained one or more electrons. An example of a common buffer is a solution of acetic acid (CH3COOH) and sodium

Buffer Action - Reaction Mechanism, Addition of Acid and Bases

Acid-Base Balance
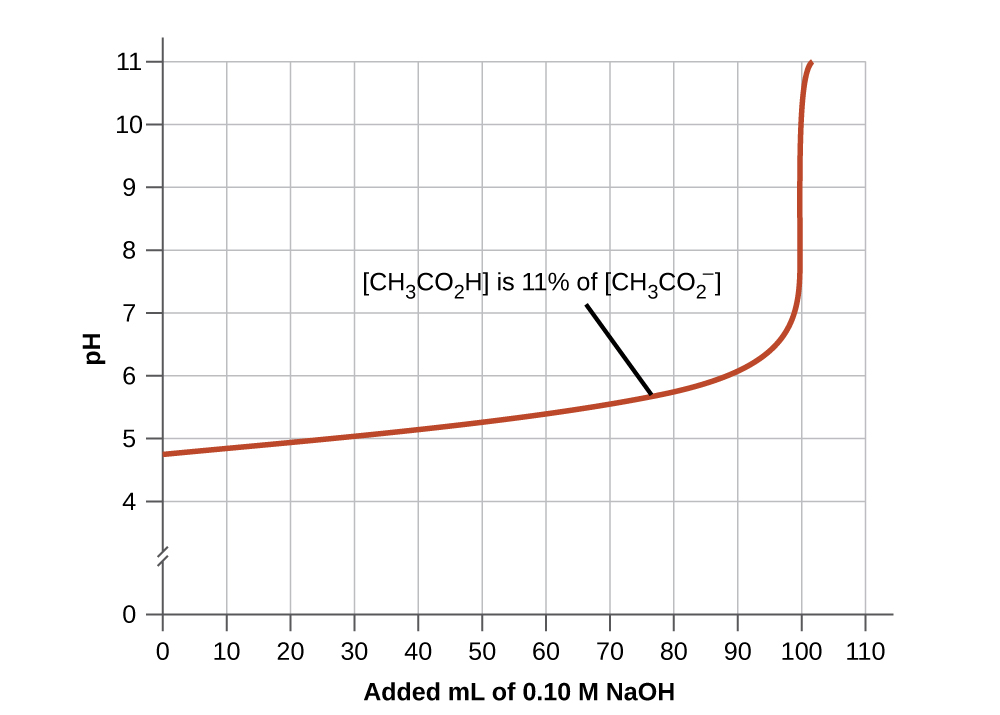
6.2 – Buffer Solutions – General Chemistry for Gee-Gees
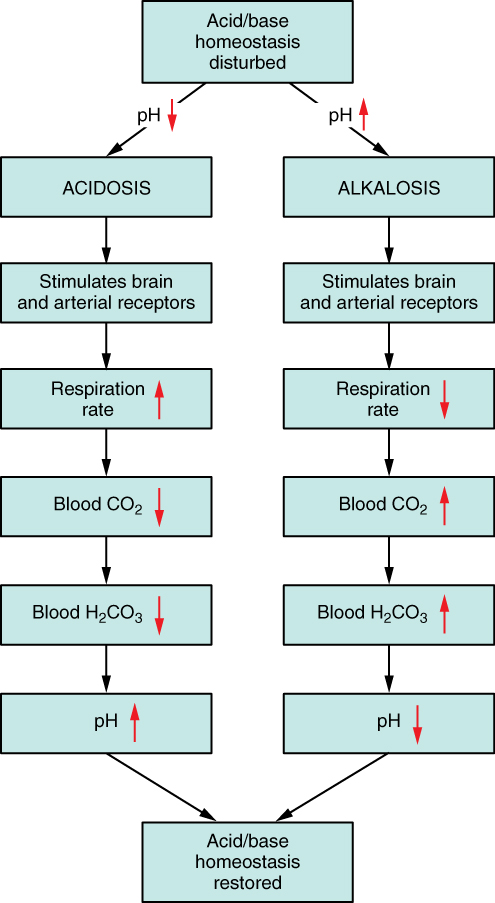
26.4 Acid-Base Balance – Anatomy & Physiology

Acid base regulation
20 Fascinating Facts About Blood Buffer

Lecture 7 (acid base balance)
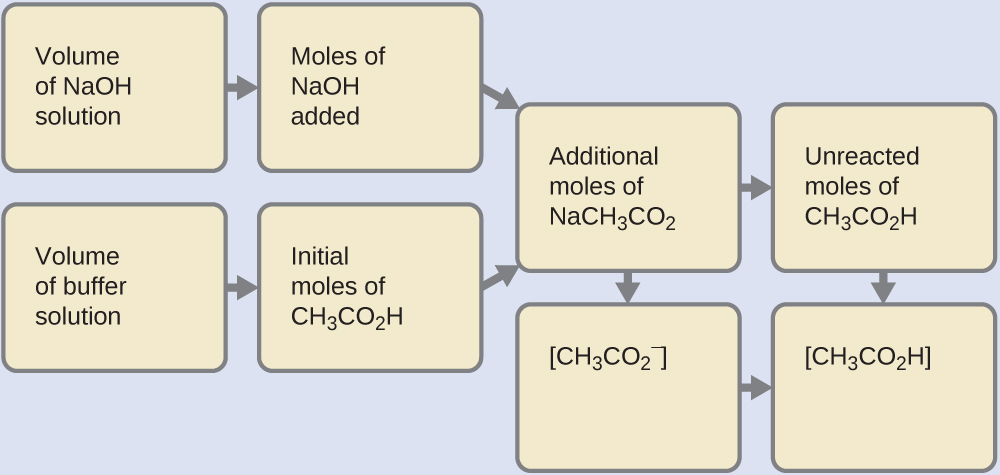
6.2 – Buffer Solutions – General Chemistry for Gee-Gees

Buffer solution - Wikipedia
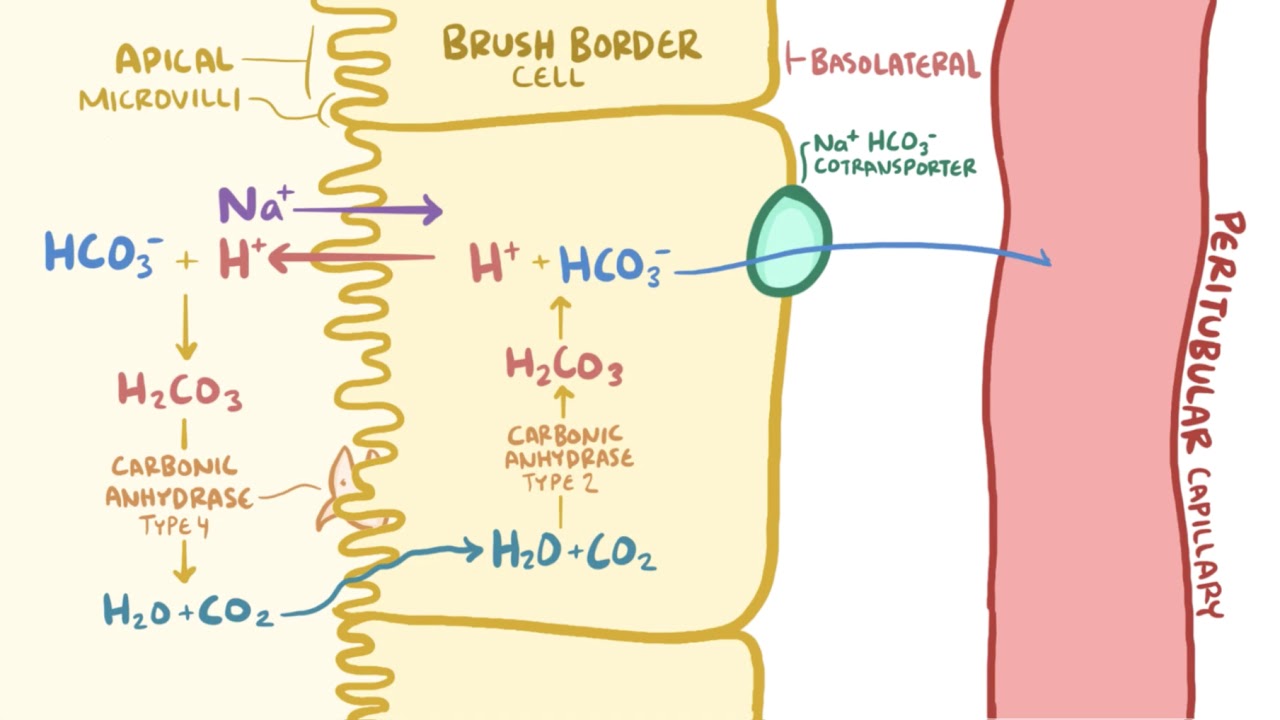
The role of the kidney in acid-base balance: Video

Acid base regulation

Buffer Region - What is a Buffer Region, Relationship between Titration and Buffer Region and How do Buffers Work along with FAQs

Buffering and Henderson-Hasselbalch equation: Video

Buffer, pH control, acid-base balance, buffer solutions

Solved 1 The most important buffer for maintaining the