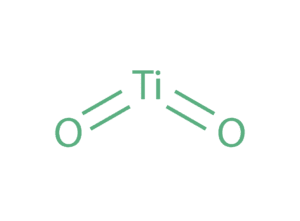
Food additive E171: findings of exposure to titanium dioxide nanoparticles
Researchers from INRA and their partners have studied the effects of oral exposure to titanium dioxide, an additive (E171) commonly used in foodstuffs, especially confectionery.

E171

Food-grade titanium dioxide (E171) induces anxiety, adenomas in colon and goblet cells hyperplasia in a regular diet model and microvesicular steatosis in a high fat diet model - ScienceDirect

The effects of exposure to titanium dioxide nanoparticles during lactation period on learning and memory of rat offspring - Abbas Mohammadipour, Mahmoud Hosseini, Alireza Fazel, Hossein Haghir, Houshang Rafatpanah, Masoume Pourganji, Alireza

Fresh concerns over titanium dioxide safety as study prompts French re-evaluation

The combined effect of food additive titanium dioxide and lipopolysaccharide on mouse intestinal barrier function after chronic exposure of titanium dioxide-contained feedstuffs, Particle and Fibre Toxicology

Tissue distribution and elimination after oral and intravenous administration of different titanium dioxide nanoparticles in rats – topic of research paper in Veterinary science. Download scholarly article PDF and read for free

Study Finds that Nanoparticle Commonly Added in Food has Adverse Effects on Gut Microbiota – Dartmouth Undergraduate Journal of Science

Titanium Dioxide—An Additive You Must Avoid!

PDF] Titanium dioxide food additive (E171) induces ROS formation and genotoxicity: contribution of micro and nano-sized fractions

Titanium dioxide food additive under review, after study finds cancer links

Titanium dioxide particles in our diet - Swiss Biohealth Clinic
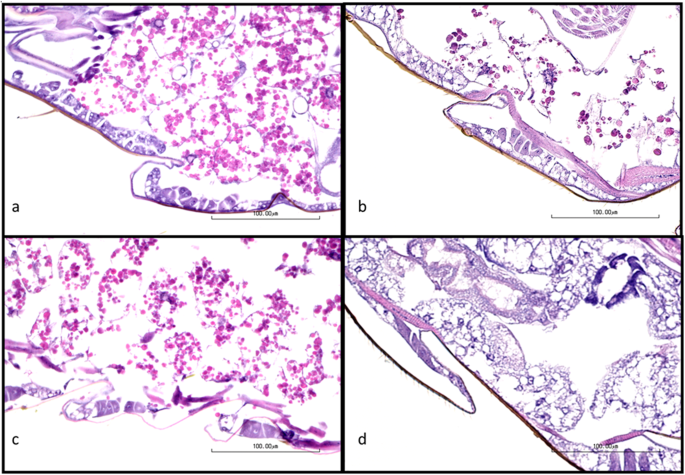
The effects of a human food additive, titanium dioxide nanoparticles E171, on Drosophila melanogaster - a 20 generation dietary exposure experiment
Full article: Characterisation of food grade titania with respect to nanoparticle content in pristine additives and in their related food products