A meta-analysis suggests that tACS improves cognition in healthy, aging, and psychiatric populations

Neurocognitive, physiological, and biophysical effects of transcranial alternating current stimulation: Trends in Cognitive Sciences
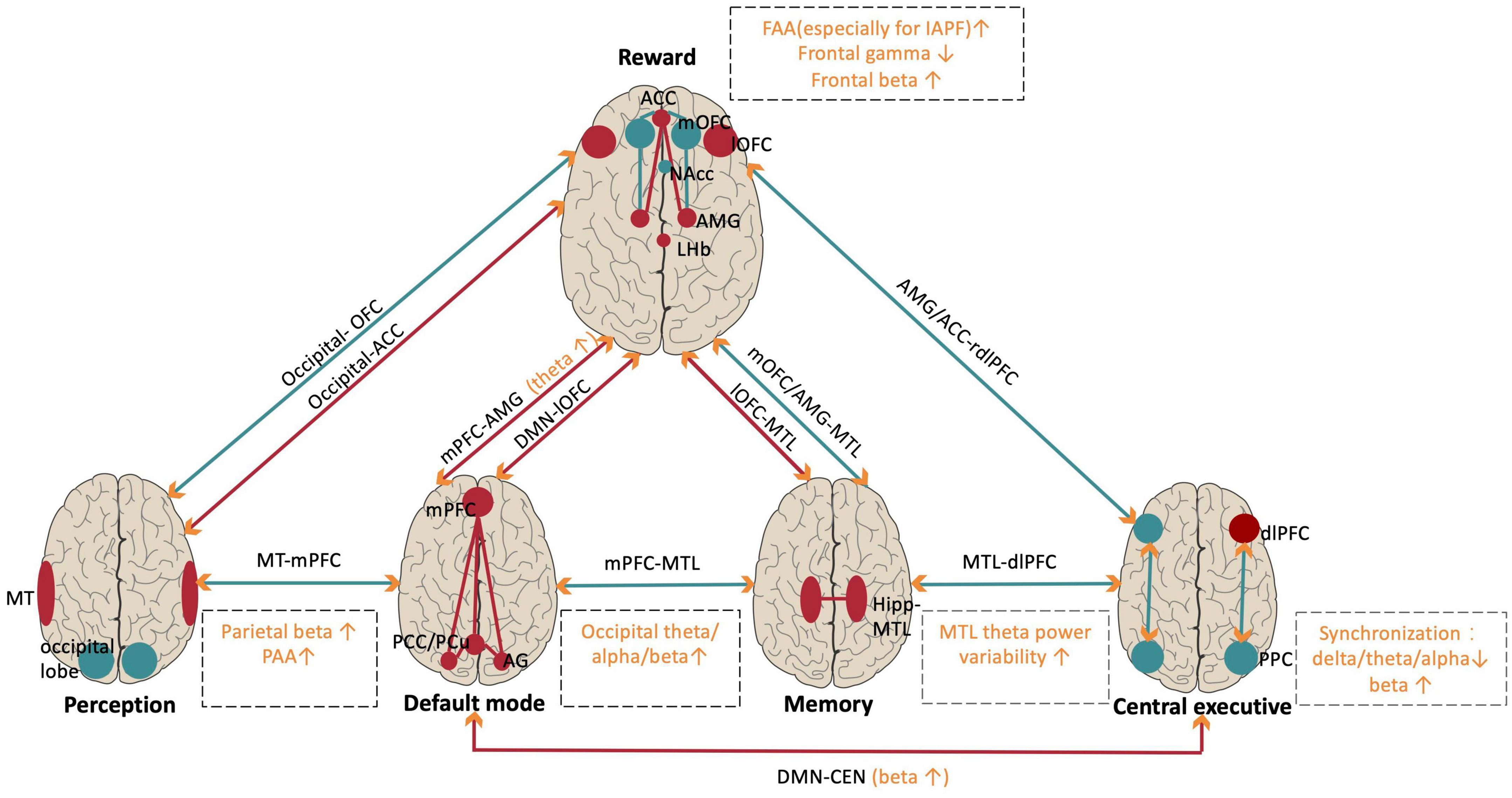
Frontiers Transcranial alternating current stimulation for the treatment of major depressive disorder: from basic mechanisms toward clinical applications

Rhythmically stimulating the brain with electrical currents could boost cognitive function, according to analysis of over 100 studies

Frontiers The moderating effects of sex, age, and education on the outcome of combined cognitive training and transcranial electrical stimulation in older adults
In-phase tACS has no effects on behavioural performance. In this figure
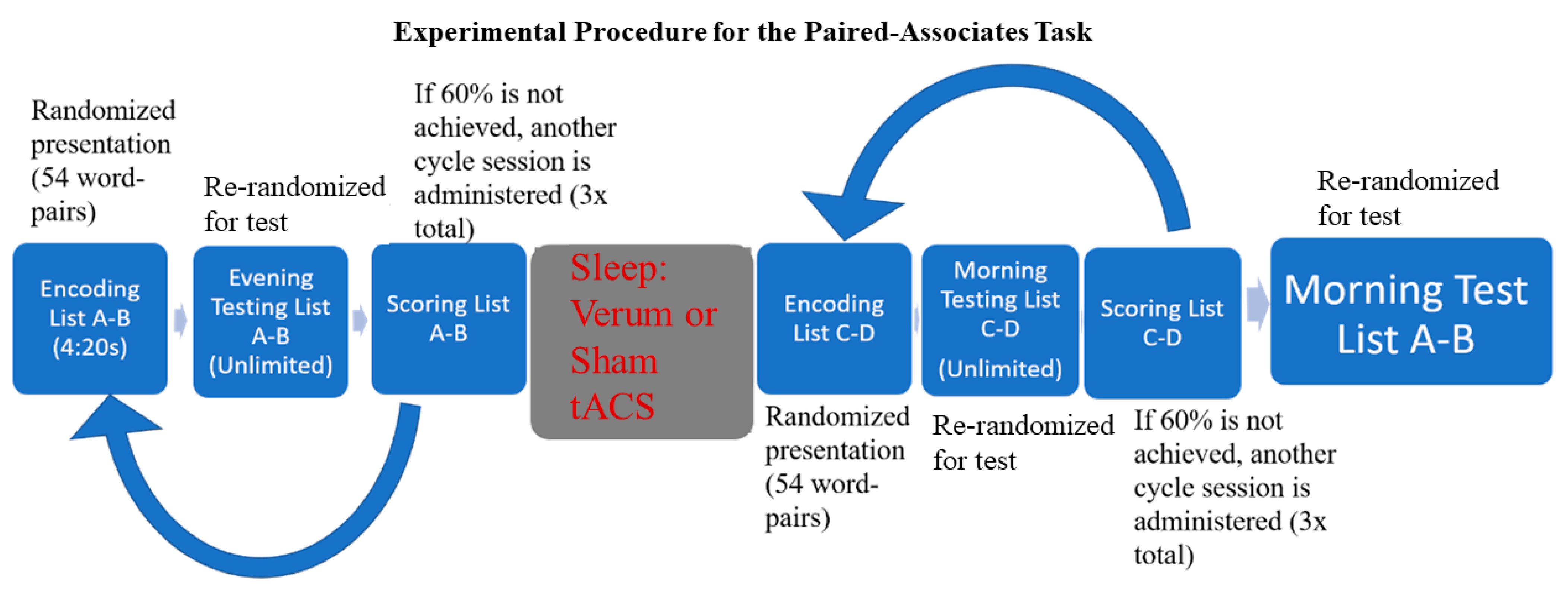
Brain Sciences, Free Full-Text

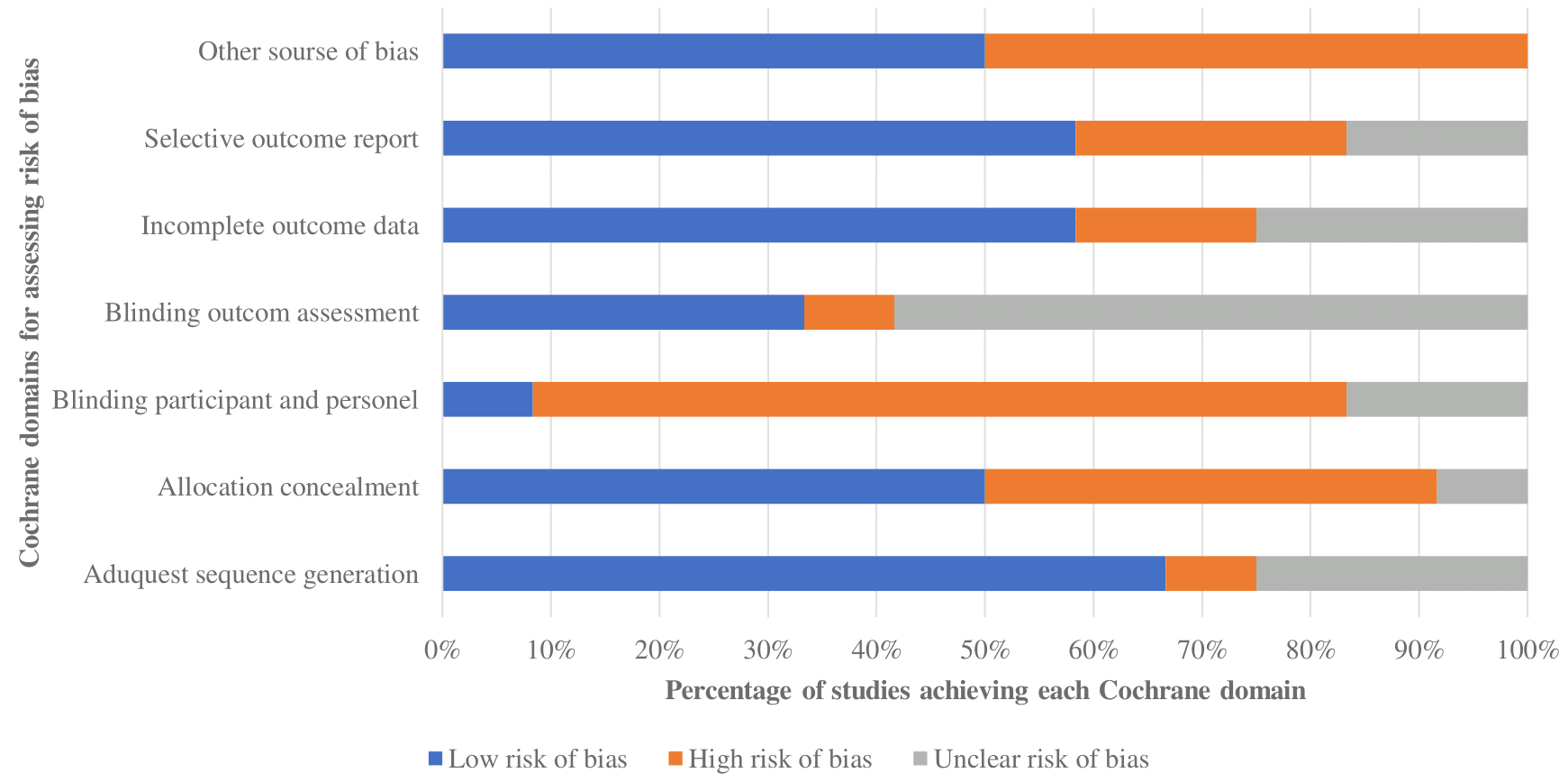
A Systematic Review of tACS Effects on Cognitive Functioning in Older Adults Across the Healthy to Dementia Spectrum

A meta-analysis suggests that tACS improves cognition in healthy, aging, and psychiatric populations

Structural and functional network mechanisms of rescuing cognitive control in aging - ScienceDirect

Jiyoung Song (@jiyoung_s) / X
Home hazard modification programs for reducing falls in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis [PeerJ]